DIAMOND
Start of the project: 01-10-2024
End of project: 30-09-2028
From 2007 to 2020, the prevalence of diagnosed diabetes rose by around 30% in the three regions, due to both an aging population and increasing obesity.
To accelerate healing and reduce the prevalence of amputations, the scientific community is seeking new technologies, such as antimicrobial delivery systems, to overcome the problems of vascularization and their poor penetration of the infected site.
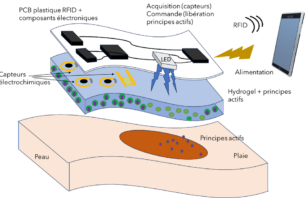
Real-time detection of biological signals indicating a healing defect using an intelligent dressing to trigger therapeutic action is a challenge.
In this project, we propose to integrate sensors as well as an electrically, optically or thermally stimulable hydrogel into the dressing, which can activate the release of encapsulated drugs or active components (anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, etc.). It's important to deliver biologically active molecules only when needed. This helps to combat bacterial multi-resistance, reduce side effects, improve healing and reduce the frequency of dressing changes.
Materia Nova has recognized expertise in the development/characterization of chemical sensors, the synthesis and formulation of biocompatible and biodegradable polymer sensors, and the encapsulation and release of biologically active substances.
Materia Nova will focus on the characterization of the sensors developed and their durability.
At the end of the project, demonstrators of these intelligent connected dressings will be produced using methods that can be transferred to companies in the field of dressings and medical devices.
The project partners:
France: University of Lille, Eurasanté
Wallonia: University of MONS, Materia Nova, Multitel
Flanders: Centexbel, University of Gent
The Diabetes League and Jolimont Hospital are associate partners.